Audit & Assurance Standards Framework
Auditing & Assurance Standards Framework Overview
This framework sets out the standards for audit and assurance engagements in
New Zealand.
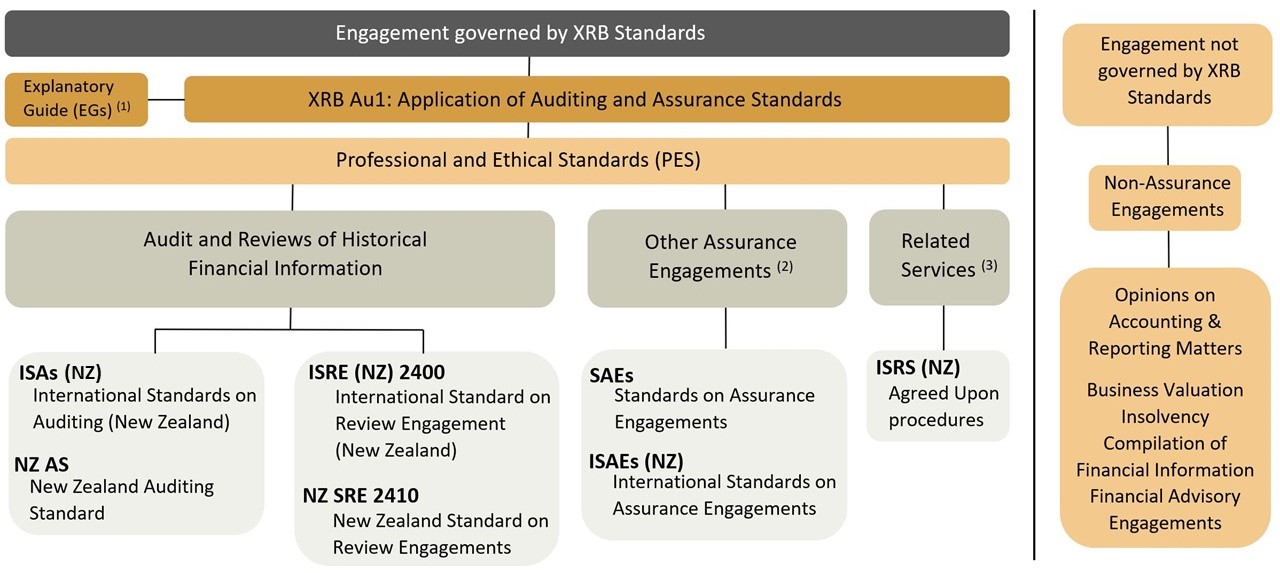
New Zealand enactments require assurance practitioners to comply with the audit and assurance standards issued by the XRB. This includes professional and ethical standards for assurance practitioners.
XRB Au1
XRB Au1 is the overarching standard which gives effect to the framework. It identifies and codifies the auditing and assurance standards that must be applied for the different types of assurance engagements and related services.
XRB Au1 establishes which standards apply when conducting an assurance engagement or related service. This includes application of:
- Professional and ethical standards when preparing and conducting an assurance engagement.
- International Standards on Auditing (New Zealand) when conducting an audit of historical financial information.
- Reviewing Engagement Standards when conducting a review of historical financial information
- Other Assurance Engagement Standards when conducting assurance engagements other than audits or reviews of historical financial information
- Related Services Standards when conducting agreed-upon procedures to information and other related services engagements as specified .
Explanatory Guide Au 1, (EG Au1) Overview of Auditing and Assurance Standards, provides further detailed information and guidance.
- The XRB’s legislative mandate is restricted to standards relating for use in assurance engagements required by statute. The Board may also issue standards relating to Other Assurance Engagements where there is no statutory requirement for assurance, provided the Minister of Commerce authorises the XRB to do so.
-
The XRB’s legislative mandate includes related services, meaning services to perform agreed-upon procedures or other non-assurance work that may ordinarily be carried out by an audit or assurance practitioner.
Explanatory Guide Au 2, (EG Au2) Overview of the Auditing and Assurance Standard Setting Process, outlines the due process that is followed by the New Zealand Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (NZAuASB), a sub-Board of the XRB, in developing and issuing auditing and assurance standards.
- Professional bodies (e.g. Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand, CPA Australia, etc.) may also require members who are assurance practitioners to comply with the XRB auditing and assurance standards (including professional and ethical standards for assurance practitioners).
- XRB standards may be applied by assurance practitioners even if there is no statutory requirement for them to do so. When applied voluntarily, all of the applicable standards need to be applied to ensure that the assurance engagement is of appropriate quality.
The XRB also issues:
- Guidance Statements and Practice Statements which provide guidance on interpreting and applying auditing and assurance standards;
- Consultation documents and exposure drafts; and
- Explanatory documents.
None of these documents have legal status.
International conformance and harmonisation of auditing & assurance standards
This sets out the principles of convergence to international standards and harmonisation with Australian auditing and assurance standards. The framework will be used for the standard-setting process in New Zealand to enhance convergence with international practice, harmonisation with Australian audit and assurance standards, as well as reduce New Zealand standard-setting costs.
Over the years, New Zealand has adopted the international auditing and assurance standards (the “clarified standards”) by way of New Zealand equivalents to those standards, expressed, for example, as ISA (NZ).
The New Zealand equivalents are in most cases substantively identical to the international standards they are based on. This approach is consistent with our strategy of adopting international standards.
Our assurance standards strategy is to continue to adopt international auditing and assurance standards to apply in New Zealand, unless there are very strong reasons why we should not.
Implementing this strategy will mean, over time, adopting New Zealand equivalents to international standards when a domestic standard currently exists.
We recognise that in adopting international standards we are committing to using that set of standards as a whole. For example, this means that not adopting one particular ISA (NZ) would mean assurance practitioners in New Zealand could not assert compliance with ISAs (NZ).
The XRB Trans-Tasman harmonisation principles allow assurance practitioners to operate in both jurisdictions within a single set of requirements and ensure a substantively common set of auditing and assurance standards that apply in both countries.
The NZAuASB and the AUASB have agreed on a common set of principles relating to the standards that each Board issues.
This co-operation contributes to the outcome framework for creating a Single Economic Market, announced by the New Zealand and Australian Prime Ministers in 2009.
The NZAuASB and AUASB are working together towards the establishment, over time, of a harmonised set of assurance standards based on international standards.
Part of this process is considering the most appropriate way to deal with country-specific requirements, including the possible use of domestic standards.
Read the international convergence and harmonisation of standards policy, combined in a single document:
The document below is an overview of the additional requirements in the Australian Auditing Standards (ASAs), not added to the New Zealand Auditing standards.
Note: this document will be subject to review in the near future and updated in accordance with any changes.
Policy Statements
This policy sets out the processes the XRB Board and sub-Boards (the NZASB and NZAuASB) will follow when auditors (or other parties) submit modified audit reports under the Companies Act 1993 and the Financial Markets Conduct Act 2013.
This policy sets out decision making processes the XRB will follow when developing PBE Standards.

